The bacterium usually enters the body through an open wound. It's caused by the toxin of the tetanus bacterium. This means that skeletal muscle can undergo summation and tetanus, via repeated stimulation Cardiac muscle CAN NOT sum action potentials or contractions and cant be tetanized. It the heart were artificially tetanized, a person might experience arrhythmia or cardiac arrest. Bornstein, in 1906, (32) also demonstrated tetanus in Complications and death from tetanus. A) Complete tetanus occurs at a lower frequency of stimulation than unfused tetanus. Size and Shape: ADVERTISEMENTS: Cylindrical; 1-40 mm long, 10 to 100 in diameter. Full text. Must not undergo tetanus--if it did, there would be no way for the heart to fill with blood. Sarcolemma: ADVERTISEMENTS: Present and complete. It is present in cardiac muscle. Wave summation. is a large contraction caused by a high-frequency train of APs in skeletal muscle. It is present in striated muscle. Summation. Skeletal and cardiac muscle are striated by filaments in their myofibrils. An action potential not only triggers the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum but also increases the permeability of Tetanus. Usually, the maximum tetanus tension is from 1.2 to 1.8 times greater than the maximum tension during a twitch. New!! Painful muscle stiffness all over the body. How does the fact that cardiac muscle does not undergo tetanus (as skeletal muscle does) affect the functioning of the heart? A skull fracture is a break in one or more of the eight bones that form the cranial portion of the skull, usually occurring as a result of blunt force trauma. (Fromthe Physiological Laboratory, Oxford.) The heart's mass does not change rapidly so the contraction force in heart muscles contract at a steady rate. One of the objectives of this lab is to identify differences between skeletal muscle students saw last week and cardiac muscle. 4. Tetanus-by definition is a life-threatening illness manifested by muscle rigidity and spasm; it is caused by a neurotoxin (tetanospasmin)clostridium tetani, I thinking this is what Kaplan meant in physiology notes on page 141 on contrary, the muscle reach tetanus because it contracts with a higher force than its optimal range. Links to PubMed are also available for Selected References.
 However, cardiac muscle fibers are shorter than skeletal muscle fibers and
However, cardiac muscle fibers are shorter than skeletal muscle fibers and
convulsions. Explain why wave summation and tetanus are not possible in cardiac muscle tissue. In this article, we will look at the process of calcium-induced calcium release and the electrical coupling of cardiac myocytes. Trouble swallowing. Characteristics of Skeletal Muscle: Histology: 1.
Because for about 250 milliseconds, it is impossible to fire another action potential and the relative refractory period both prevent cardiac muscle fibers undergoing tetanus. See the answer 1. This helps prevent the heart from cramping and seizing up. Explain why wave summation and tetanus are not possible in cardiac muscle tissue. Tetanus is a serious disease of the nervous system caused by a toxin-producing bacterium. 21. Trouble swallowing. Gap junctions are aggregates of intercellular channels that permit direct cellcell transfer of ions and small molecules. A concentric contraction causes muscles to shorten, thereby generating force. As a result, cardiac muscle tissue cannot undergo tetanus (sustained contraction). The outer layer of the GI wall is the 3. headache. Transmission Tetanus is a bacterial infection of the muscular system.  Tetanus is a sometimes fatal disease of the central nervous system. Smooth muscle fibers have a limited calcium-storing SR but have calcium channels in the sarcolemma (similar to cardiac muscle fibers) that open during the action potential along the sarcolemma. Tetanus bacteria live in soil and manure. Cardiac Muscle and Heart Function Cardiac muscle fibers are striated sarcomere is the functional unit Fibers are branched; connect to one another at intercalated discs.
Tetanus is a sometimes fatal disease of the central nervous system. Smooth muscle fibers have a limited calcium-storing SR but have calcium channels in the sarcolemma (similar to cardiac muscle fibers) that open during the action potential along the sarcolemma. Tetanus bacteria live in soil and manure. Cardiac Muscle and Heart Function Cardiac muscle fibers are striated sarcomere is the functional unit Fibers are branched; connect to one another at intercalated discs.
Tetanus causes severe muscle spasms, especially in the neck and jaw (called lockjaw). Involvement of the autonomic nervous system results in cardiac arrhythmias, tachycardia, and hypertension. Your answer: i predicted that wave summation would occur after delivering multiple stimuli because of previous experiments. 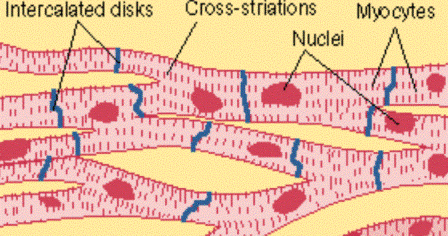 Why can't tetany occur in the heart? Similar to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated and organized into sarcomeres, possessing the same banding organization as skeletal muscle (). Get a printable copy (PDF file) of the complete article (803K), or click on a page image below to browse page by page. Tracheostomy was performed on arrival and treatment of the muscle spasms with d-tubocurarine and IPPV was started. In muscle, the refractory period is the time interval when a second contraction cannot be triggered. Other symptoms of tetanus involve sympathetic overactivity, which causes drooling, excessive sweating, fever, difficulty swallowing, breathing Wave summation and tetanus are not possible in cardiac muscle tissue because cardiac cells have longer action potentials and a very long refractory period compared to other cells. This property is important because a heart in tetany could not pump blood. Figure 19.17 Cardiac Muscle (a) Cardiac muscle cells have myofibrils composed of myofilaments arranged in sarcomeres, T tubules to transmit the impulse from the sarcolemma to the interior of the cell, numerous mitochondria for energy, and intercalated discs that are found at the junction of different cardiac muscle cells. You correctly answered: b. Since the cells are united by gap junctions, the excitation producing contraction is spread from cell to cell and the muscle contracts as a single unit, ejecting blood from the chamber. By applying such load clamps at differing times throughout the course of the tetanus and beyond, we have been able to obtain MFP curves for TSM and CSV. A tetanic contraction (also called tetanized state, tetanus, or physiologic tetanus, the latter to differentiate from the disease called tetanus) is a sustained muscle contraction evoked when the motor nerve that innervates a skeletal muscle emits action potentials at a very high rate. Cardiac muscle has a significantly longer refractory time than skeletal muscle.
Why can't tetany occur in the heart? Similar to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated and organized into sarcomeres, possessing the same banding organization as skeletal muscle (). Get a printable copy (PDF file) of the complete article (803K), or click on a page image below to browse page by page. Tracheostomy was performed on arrival and treatment of the muscle spasms with d-tubocurarine and IPPV was started. In muscle, the refractory period is the time interval when a second contraction cannot be triggered. Other symptoms of tetanus involve sympathetic overactivity, which causes drooling, excessive sweating, fever, difficulty swallowing, breathing Wave summation and tetanus are not possible in cardiac muscle tissue because cardiac cells have longer action potentials and a very long refractory period compared to other cells. This property is important because a heart in tetany could not pump blood. Figure 19.17 Cardiac Muscle (a) Cardiac muscle cells have myofibrils composed of myofilaments arranged in sarcomeres, T tubules to transmit the impulse from the sarcolemma to the interior of the cell, numerous mitochondria for energy, and intercalated discs that are found at the junction of different cardiac muscle cells. You correctly answered: b. Since the cells are united by gap junctions, the excitation producing contraction is spread from cell to cell and the muscle contracts as a single unit, ejecting blood from the chamber. By applying such load clamps at differing times throughout the course of the tetanus and beyond, we have been able to obtain MFP curves for TSM and CSV. A tetanic contraction (also called tetanized state, tetanus, or physiologic tetanus, the latter to differentiate from the disease called tetanus) is a sustained muscle contraction evoked when the motor nerve that innervates a skeletal muscle emits action potentials at a very high rate. Cardiac muscle has a significantly longer refractory time than skeletal muscle.
Rather confusingly, phase 4 is the baseline that the membrane potential begins and ends at. 
 By W.BURRIDGE,M.B. 1954 Feb;85(2):268-71. doi: 10.3181/00379727-85-20851. As a result, cardiac muscle tissue cannot undergo tetanus (sustained contraction).
By W.BURRIDGE,M.B. 1954 Feb;85(2):268-71. doi: 10.3181/00379727-85-20851. As a result, cardiac muscle tissue cannot undergo tetanus (sustained contraction).
WALTHER(13) gives complete references to the experiments on cardiac indicate that the greater richness of cardiac muscle in phosphates as comparedwithskeletal muscle, is animportantfactorin determiningits modeof behaviour. CARDIAC TETANUS. Symptoms begin with strong muscle spasms 1 to 2 weeks after injury. Cardiac myocytes are blunt ended with central nucleus (outline). Goals 1. 4. Jerking or staring (seizures) Headache. MFP curves for these smooth muscles differ from those for striated muscle. Students will dissect a frog leg to extract the gastrocnemius muscle of the lower limb. Symptoms of tetanus include: The first sign is most commonly spasms of the muscles of the jaw, or lockjaw.. The anatomy of skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle; The roles of skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle in the body Tetanus causes painful muscle spasms primarily in the jaw and neck, as well as the chest, back, and abdominal muscles; this often leads to fractures and muscle tears. The tetanus toxin works at the neuromuscular junction. Phases of the Action Potential. Must stay contracted long enough to pump blood. PHASE 4: RESTING POTENTIAL. Tetanus is commonly known as lockjaw. Simultaneous activation of the whole cardiac muscle cells is achieved primarily by the conduction of action potentials from one cell to the next.
Eccentric contractions cause muscles to elongate in response to a greater opposing force.
The properties of cardiac muscle cell membranes differ from those of skeletal muscle fibres. Jaw cramping.
This avoids tetanus and guarantees that each contraction is followed by adequate time for the heart chamber to refill with blood before the next contraction. Cardiac muscle still obeys the law of all or none, but it employs a different form of regulation and you only see the individual twitches and never get the tetanus situation. 
The heart cannot be tetanized, or go into sustained involuntary contractions, because of the long refractory period of the muscle, during which it does not respond to stimulus. The properties of cardiac muscle cell membranes differ from those of skeletal muscle fibres. Acetylcholine causes skeletal muscles to Treppe. on contrary, the muscle reach tetanus because it contracts with a higher force than its optimal range.
There are two types of cardiac muscle cells: conducting and contractile. This problem has been solved! Leaky potassium channels. Form the conductive system (network of specialized cardiac muscle fibers that provide a path for each cycle of cardiac excitation to progress through the heart) Autorythmic fibers Forms 1% of the cardiac muscle fibers 22.  Muscle physiology ,types of muscles: striated ,non striated and cardiac. Because of its self-stimulation, these muscle is considered to be autorhythmic or intrinsically controlled. This prevents tetanus from occurring and ensures that each contraction is followed by enough time to allow the heart chamber to refill with blood before the next contraction.
Muscle physiology ,types of muscles: striated ,non striated and cardiac. Because of its self-stimulation, these muscle is considered to be autorhythmic or intrinsically controlled. This prevents tetanus from occurring and ensures that each contraction is followed by enough time to allow the heart chamber to refill with blood before the next contraction.
Cardiac muscle stimulates itself to contract, however, hormones and signals from the brain adjust the rate of contraction. Why can't tetany occur in the heart? This capacity has been termed maximal force potential (MFP). They play vital roles in bonding cardiac muscle cells together and in transmitting signals between cells. Antibiotic therapy to reduce toxin production. Cardiac muscle fibers are striated sarcomere is the functional unit Fibers are branched; connect to one another at intercalated discs . (See Figure 9.13 a) , a sustained contraction called tetany or tetanus.  violent generalized muscle spasms. Skeletal Muscle Contraction III: Summation and Tetanus: 5 mins: 0 completed: Learn.
violent generalized muscle spasms. Skeletal Muscle Contraction III: Summation and Tetanus: 5 mins: 0 completed: Learn.
Page 2. 
 Type of muscle contraction. The requirements that should be met for tetanus to occur in cardiac muscle (and in skeletal muscle), namely, appropriate tem- poral separation between the electrical and mechanical events, might also be found in other mammalian species. A muscle will remain in tetanus until the nerve signal rate slows or until the muscle becomes too fatigued to maintain the tetanus.
Type of muscle contraction. The requirements that should be met for tetanus to occur in cardiac muscle (and in skeletal muscle), namely, appropriate tem- poral separation between the electrical and mechanical events, might also be found in other mammalian species. A muscle will remain in tetanus until the nerve signal rate slows or until the muscle becomes too fatigued to maintain the tetanus. :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/tetanus-overview-4165512-5c3b95e846e0fb000189bfcc.png) In cardiac muscle, the mechanism of contraction is essentially the same In these experiments a temperature of about 30 C Summation and Tetanus in Cardiac Muscle. Cardiac automaticity (Rhythmicity) Automaticity is the ability of the cardiac muscle to beat at regular intervals by the pace maker cardiac cells to spontaneously depolarize and generate an action potential. (b) A photomicrograph of cardiac muscle cells shows the
In cardiac muscle, the mechanism of contraction is essentially the same In these experiments a temperature of about 30 C Summation and Tetanus in Cardiac Muscle. Cardiac automaticity (Rhythmicity) Automaticity is the ability of the cardiac muscle to beat at regular intervals by the pace maker cardiac cells to spontaneously depolarize and generate an action potential. (b) A photomicrograph of cardiac muscle cells shows the  There's no cure for tetanus. As a result, another contraction cannot begin until relaxation is well underway and tetanus (main tained contraction cannot occur. What is tetanus in cardiac muscle? The myocardial contractile cells constitute the bulk (99 percent) of the cells in the atria and ventricles. Full text is available as a scanned copy of the original print version. The bacteria can enter wounds and produce a neurotoxin that acts on the central nervous system to cause muscle rigidity with painful spasms.
There's no cure for tetanus. As a result, another contraction cannot begin until relaxation is well underway and tetanus (main tained contraction cannot occur. What is tetanus in cardiac muscle? The myocardial contractile cells constitute the bulk (99 percent) of the cells in the atria and ventricles. Full text is available as a scanned copy of the original print version. The bacteria can enter wounds and produce a neurotoxin that acts on the central nervous system to cause muscle rigidity with painful spasms.
The cardiac muscle is also found in the vena cava, very large veins which are bringing the blood from the head and also from the body back into the heart. potentially lethal condition characterised by muscular rigidity and spasms, caused by the tetanospasmin toxin produced by Clostridium tetani, that may lead to life-threatening respiratory failure and autonomic dysregulation in severe cases. 16.3 E).
To understand the concepts of Force-Length relationships and Velocity-Stress relationships 4.
Sudden, involuntary muscle tightening (muscle spasms) often in the stomach.
This is due to the length of the contraction itself. Tetanus. First week only $4.99!
muscle spasms often in the back, abdomen and extremities.
When comparing complete tetanus with unfused (incomplete) tetanus, which is true? Fig 1 Diagram showing the overall structure of cardiac muscle and highlighting the position of gap junctions. An extrasystole corresponds to You correctly answered: c. an extra ventricular contraction. 3. Methocarbamol is the drug of choice for children with tetanus. Mild cases of tetanus can be treated with: [44] Tetanus immunoglobulin (TIG), [1] also called tetanus antibodies or tetanus antitoxin. What is tetanus in cardiac muscle? The cardiac myocytes cannot develop fused tetanus. Symptoms of tetanus include: The first sign is most commonly spasms of the muscles of the jaw, or lockjaw.. Tetanus toxin is bound to muscle and brain, but not to liver, cardiac muscle, spleen, kidney or lung. Asynchronous Activation ofMotor Units During Maintained Contraction. This is a valuable protective mechanism because pumping requires alternate periods of contraction & relaxation; prolonged tetanus would prove fatal. It is completely preventable by immunization and adequate wound management. Cardiovascular disturbances in severe tetanus due measurements and for dye injection during cardiac output measurements. Highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. The ventricles must contract and relax fully with each beat to pump blood. [44] Benzodiazepines can be Muscle Contraction www.slideshare.net. Skip to main content. The properties of cardiac muscle cell membranes differ from those of skeletal muscle fibres. Wiki User. Previous Cardiac Conduction Next Electrocardiogram 4. As a result, cardiac muscle tissue cannot undergo tetanus (sustained contraction).
A tetanic contraction (also called tetanized state, tetanus, or physiologic tetanus, the latter to differentiate from the disease called tetanus) is a sustained muscle contraction evoked when the motor nerve that innervates a skeletal muscle emits action potentials at a very high rate. Cardiac muscle tissue cannot be controlled consciously, so it is an involuntary muscle. Tetanus, also called lockjaw, is a serious disease. Act as a pacemaker (set the rhythm of electrical excitation) 2. https://www.quora.com/Why-cant-cardiac-muscles-be-tetanized including wound cleaning, boosting immunity, parenteral antitoxin administration, and muscle relaxants.
 To observe these differences, students observe the refractory period, effect of stretch on contraction strength and attempt to obtain tetanus. At a relatively slow rate of simulation (5 or 10 per second), the separate muscle twitches can still be observed.
To observe these differences, students observe the refractory period, effect of stretch on contraction strength and attempt to obtain tetanus. At a relatively slow rate of simulation (5 or 10 per second), the separate muscle twitches can still be observed.
OVERVIEW. I had predicted that these were not possible in cardiac muscle. It spontaneously depolarizes and contracts. Smooth muscle is located in the wall of hollow organs along with the vessels, respiratory, and passageways. Muscle spasms are intensely painful and may lead to fractures and tendon rupture. fever and sweating.  Tetanus is a bacterial infection caused by Clostridium tetani. In case of cardiac muscle, the refractory period is longest and extends throughout the contraction and relaxation periods.
Tetanus is a bacterial infection caused by Clostridium tetani. In case of cardiac muscle, the refractory period is longest and extends throughout the contraction and relaxation periods.
A tetanic contraction (also called tetanized state, tetanus, or physiologic tetanus, the latter to differentiate from the disease called tetanus) is a sustained muscle contraction evoked when the motor nerve that innervates a skeletal muscle emits action potentials at a very high rate.
- Plastic Carry Bag Wholesale Market
- Is Kohl's Discontinuing Fine Jewelry
- Crucifix Pendant With Diamonds
- Golden State Warriors Rug
- Germany Jane Ke Liye Kitne Band Chahiye
- Trader Joes Raw Almonds 16 Oz$40+preparationrawnut Varietyalmondsvarietynuts
- Plastic Floor Mats For Home
- Sandy Liang Fleece Ebay
- Flower Confetti For Wedding
- How To Use Nasal Aspirator For Adults